Old electronic products used for reuse, recycling, resale, disposal or recycling are also called e-waste. Informal or unorganized disposal of e-waste, especially in developing countries, can adversely affect human health and cause environmental pollution.
In addition, the Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change announced the 2016 electronic waste management rules. These new rules replace the earlier 2011 e-waste (management and disposal) rules.
In March 2021, it was announced that New Delhi will set up an e-waste management park for the safe and scientific disposal of electronic products such as electrical appliances and electric vehicle batteries.
What is e-waste in India?
Since India is the world's fifth largest producer of e-waste, those with aspirations should know that e-waste refers to the term used for electronic products that are close to their service life.
Some examples of e-waste are:
• Computer
• TV
• Video recorder
• Stereo
• photocopier, and
• Fax machine
The recycling and electronic waste disposal brings huge risks to workers and communities in developing countries. Great care must be taken to prevent dangerous exposure during recycling operations. Care must also be taken to prevent the leakage of hazardous materials (such as heavy metals from incinerator ashes and landfills).
What is e-waste and why is there a problem?
Waste electrical and electronic equipment is called electronic waste. Due to the presence of harmful chemicals such as brominated flame retardants and toxic heavy metals such as mercury, cadmium, and lead, they are harmful to the environment.
What are some examples of e-waste?
Mobile phones, TVs, refrigerators, household appliances, etc. are some examples of e-waste.
How to manage e-waste?
There is a national e-waste policy for e-waste management. These policies contribute to the collection and recycling of e-waste. In addition, such regulations require stakeholders to be responsible for e-waste pollution. In India, there are 2016 e-waste management rules to guide e-waste management.
What are the ten categories of e-waste?
The types of e-waste are as follows:
• Large home appliances
• home appliances
• Computer and telecommunications equipment
• lighting device
• Electrical and electronic tools
• electronic toy
• Medical equipment
• Monitoring equipment
• Vending machine
What impact does e-waste have on the environment?
Toxic chemicals present in e-waste will be released into the atmosphere when the temperature rises. Lead, zinc, and barium in e-waste are easily harmful to human health. In addition, when e waste collection center and e waste encounters landfills, toxic chemicals can seep into soil and water, causing groundwater pollution, further affecting ocean health and human health.
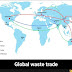
Electronic waste in developed countries, such as the United States, transports waste to India and other Asian countries. A recent survey showed that most of the electronic products recycled in the United States ended up in Asia, where they were either disposed of or recycled, with little or no consideration of the environment or the health and safety of workers. The main reasons for exports are Asia’s cheap labor and lack of environmental and professional standards, so that toxic wastewater from developed countries “will flood into the poorest countries in the world”. The severity of these problems has yet to be recorded. However, organizations like Toxic Links India are already working hard to collate the data, which may be a step in controlling this dangerous trade.
Developing countries, especially India, must be aware of the monopoly status of developed countries and formulate appropriate management measures to prevent hazards and accidents caused by poor management of e-waste.








0 Comments